OS agent
Implementation is done through OS agent running on each Oracle Solaris host (LDOM/CDOM/Global Zone/Zone).
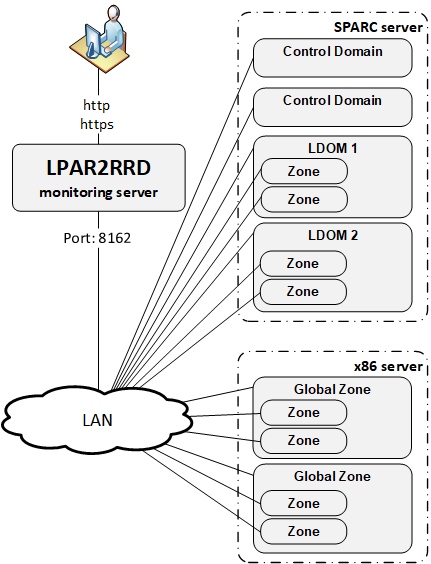
2) brings you more details about each LDOM.
3) monitoring all Zones from OS point of view.
You might need to add lpar2rrd user into /etc/cron.allow (Linux) or /var/adm/cron/cron.allow (AIX) if 'crontab -e' command fails
Allow it for lpar2rrd user as root user.
You will see your Solaris boxes in the UI under Solaris folder within an hour (Ctrl-F5 in the web browser).

Working modes
- install OS agents on all Control Domains (CDOM) only
- Install OS agents on all LDOMs and Global Zones
- Install OS agents on all LDOMs and Global Zones and Zones
2) brings you more details about each LDOM.
3) monitoring all Zones from OS point of view.
Installation summary
- Assure your network allows TCP connection initiated from OS agents to XorMon server on port 8162
- Install the OS agent on all LDOMs, CDOMs and Global Zones
- Optionally install the OS agent on all Zones to get additional OS based metrics
OS agent install on a LDOM/CDOM
- Create user lpar2rrd with role solaris.ldoms.read
- Installation under root:
# gunzip lpar2rrd-agent-6.00-0.solaris-sparc.tar.gz # tar xf lpar2rrd-agent-6.00-0.solaris-sparc.tar # pkgadd -d . The following packages are available: 1 lpar2rrd-agent LPAR2RRD OS agent 6.00 ...
Upgrade (remove original package at first then install the new one):# pkgrm lpar2rrd-agent # pkgadd -d .
- Assign LDOM/CDOM read rights solaris.ldoms.read for the user (lpar2rrd) which will run the agent:
# usermod -A solaris.ldoms.read lpar2rrd
Assure that rights are fine, "/sbin/ldm ls -p" should not return "Authorization failed"# su - lpar2rrd $ /sbin/ldm ls -p
OS agent install on Zone/Global Zone
-
Use any unprivileged user (lpar2rrd preferably) for agent install and run.
Use same Solaris package like in LDOM example above.
Use Solaris x86 package on that platform: lpar2rrd-agent-6.00-0.solaris-i86pc.tar
Testing connection
- Test connection to the XorMon server
$ /usr/bin/perl /opt/lpar2rrd-agent/lpar2rrd-agent.pl -d <XorMon-SERVER> ... OS agent working for server: <XorMon-SERVER> store file for sending is /var/tmp/lpar2rrd-agent-<XorMon-SERVER>-lpar2rrd.txt
It means that data has been sent to the server, all is fine
Here is example when the agent is not able to sent data :$ /usr/bin/perl /opt/lpar2rrd-agent/lpar2rrd-agent.pl -d <XorMon-SERVER> ... OS agent working for server: <XorMon-SERVER> store file for sending is /var/tmp/lpar2rrd-agent-<XorMon-SERVER>-lpar2rrd.txt Agent timed out after : 50 seconds /opt/lpar2rrd-agent/lpar2rrd-agent.pl:265
It means that the agent could not contact the server.
Check communication (if firewalls are open), DNS resolution of the server etc.
Schedule OS agent in Solaris lpar2rrd's crontab
# su - lpar2rrd $ crontab -e * * * * * /usr/bin/perl /opt/lpar2rrd-agent/lpar2rrd-agent.pl <XorMon-SERVER> > /var/tmp/lpar2rrd-agent.out 2>&1Replace <XorMon-SERVER> by hostname of your XorMon server.
You might need to add lpar2rrd user into /etc/cron.allow (Linux) or /var/adm/cron/cron.allow (AIX) if 'crontab -e' command fails
Allow it for lpar2rrd user as root user.
# echo "lpar2rrd" >> /etc/cron.allow
XorMon is able to monitor stand-alone MS Windows servers and MS Hyper-V performance metrics (hosts and VMs).
Implementation is done through single Windows OS agent running on any Windows host in the Windows domain.
This OS agent gets all required configuration from the AD and performance data of monitored hosts through WMI.
It passes such data to XorMon server where data is saved and presented.
Is used LPAR2RRD Windows OS agent which works everywhere where is available PowerShell 3 and higher
It does not directly depends on the Windows version, if you are able to upgrade PowerShell to 3.0+ on older machines then it will work.
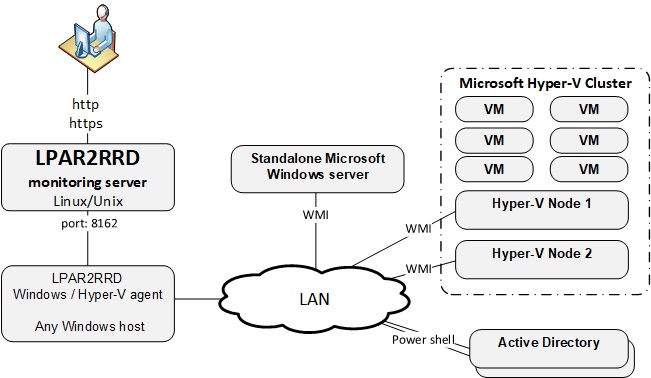
Installation summary
- Allow TCP connection initiated from Windows LPAR2RRD Hyper-V agent server to XorMon server on port 8162
- PowerShell version 3 and higher only is supported on Windows hosts
User creation
- Create the user in the AD with membership in these groups:
- Event Log Readers
- Hyper-V Administrators
- Performance Log Users
- Performance Monitor Users
- Set rights in GPO and AD using this manual
- Give local admin rights to the the user on the Win server where LPAR2RRD Hyper-V agent will be running.
Add him into Domain Users group.
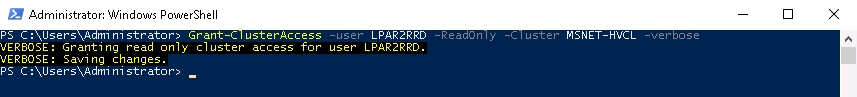
- Assign read-only rights for monitored Hyper-V clusters to the user
OS agent installation
- Setup.vbs
- Configuration.vbs
- LPAR2RRD-agent.ps1
- LPAR2RRD-agent-Configuration.ps1
- LPAR2RRD-agent-Installer.ps1
| Unzip LPAR2RRD-Win-agent-1.3.3.zip |
Unblock these files by right clicking them and checking "Unblock"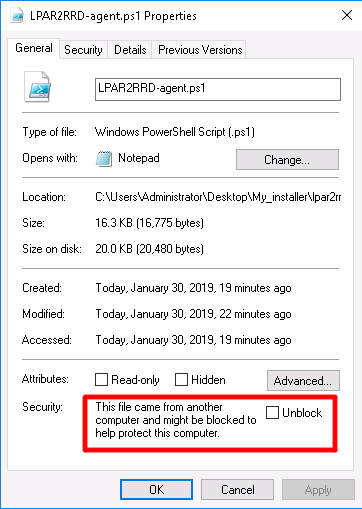 |
When 'Unblock" does not help and installation does not start (install windows immediatelly disapears), you might need to Set-ExecutionPolicy to enable running powershell for current user. |
Run Setup.vbs |
Select installation directory 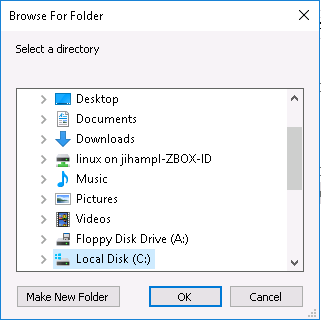 |
Put hostname of the XorMon server 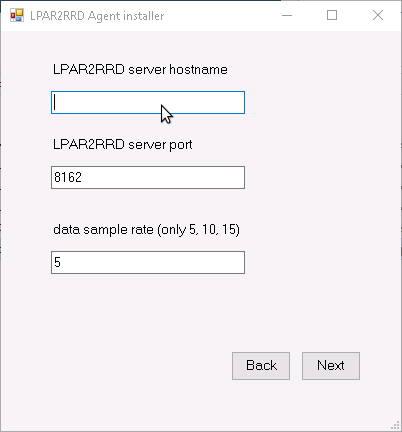 |
Test connection to the XorMon server 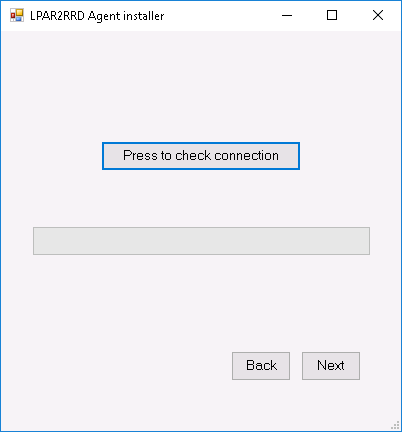 |
Put user which will run LPAR2RRD OS agent on this machine 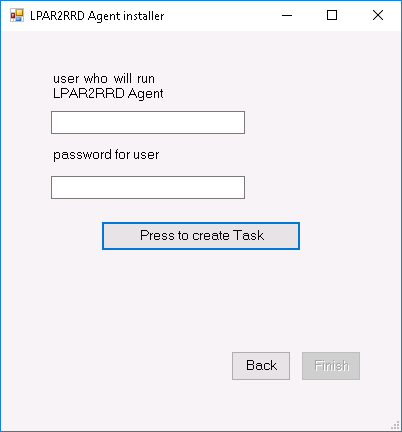 |
Select monitored mode (agent v1.3.3+) 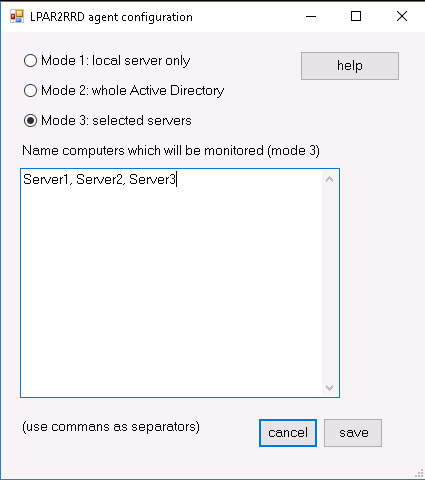 |
-
You can also use manuall OS agent installation
In case of a cluster: add there cluster name and names of all nodes as well like: cluster1,node1,node2,cluster2,node...
- Wait about 30 minutes, then Ctrl-F5 in your XorMon UI and you should see Hyper-V folder in the main menu
Monitored modes
-
The agent can run in these modes:
- leave it in default mode and monitor just the server where it is installed
- monitor all visible servers from AD
- monitor only specific servers (recommended), added into cfg file
for monitoring of cluster - add its name to servers/nodes too like: cluster1,node1,node2,cluster2,node...
OS agent is add-on feature for monitoring from operating system level.
It is monitoring CPU, memory utilization, paging, LAN and SAN traffic on all adapters.
It requires the OS agent deployment to every monitored LPAR.
The agent is written in Perl and calls basic OS commands to obtain required statistics like vmstat, lparstat and svmon.
You can even use already installed LPAR2RRD agents and direct them to XorMon host.
Operating systems
- AIX 5.1+
- Linux on Power
- Linux x86
Implementation
it is implemented as a simple client/server application.There is XorMon daemon listening on the host where XorMon server is running on port 8162.
Each LPAR has a simple Perl-based agent installed. This agent is started every minute from the crontab and saves memory and paging statistics into a temporary file.
The agent contacts the server randomly every 10-20 minutes and sends all locally stored data for that period.
Usage
perl ./lpar2rrd-agent.pl [-d] [-x] <XorMon server hostname/IP>[:<PORT>] -d forces sending out data immediately to check communication channel (DEBUG purposes) -m using sudo for multipath (only root can run it): sudo multipath -l", put this into sudoers: lpar2rrd ALL = (root) NOPASSWD: /usr/sbin/multipath -ll -x use Transport Layer Security (TLS) no option - agent collects & sends standard OS agent dataCrontab entry for scheduling, use non-admin account preferably
* * * * * /usr/bin/perl /opt/lpar2rrd-agent/lpar2rrd-agent.pl <XorMon server hostname/IP> > /var/tmp/lpar2rrd-agent.out 2>&1The agent collects data and sends them every 5 - 20 minutes to the XorMon server
If you use other than standard XorMon port, then add it after SERVER, separated by the ':' delimiter
* * * * * /usr/bin/perl /opt/lpar2rrd-agent/lpar2rrd-agent.pl <XorMon server hostname/IP>:<PORT> > /var/tmp/lpar2rrd-agent.out 2>&1If you want to send data to more XorMon server instances (number is not restricted)
* * * * * /usr/bin/perl /opt/lpar2rrd-agent/lpar2rrd-agent.pl <XorMon server 1 hostname/IP> <XorMon server 2 hostname/IP> > /var/tmp/lpar2rrd-agent.out 2>&1
Prerequisites
- Perl on each VM (each OS already contains it, no special modules are necessary)
- Opened TCP communication between each VM / LPAR and XorMon server on port 8162.
Connections are initiated from VMs / LPARs side. -
Create preferable dedicated user xormon on each host with minimum rights
# useradd -s /usr/bin/ksh -c "XorMon agent user" -m xormon
-
In case of IBM Power Systems VIO server do not use padmin account and mkuser cmd, that would not work!
Create the account under root in the same way as on usual AIX (like above useradd).
OS agent installation (client)
-
Get the latest OS agent from download page
- Linux RedHat, Rocky
# rpm -Uvh lpar2rrd-agent-7.60-0.noarch.rpm # rpm -qa|grep lpar2rrd-agent lpar2rrd-agent-7.60-0
- AIX / VIOS
# rpm -Uvh lpar2rrd-agent-7.60-0.ppc.rpm # rpm -qa|grep lpar2rrd-agent lpar2rrd-agent-7.60-0
- Linux Debian
# apt-get install ./lpar2rrd-agent_7.60-0_all.deb lpar2rrd-agent-7.60-0
- Schedule its run every minute from the crontab on every LPAR.
This line must be placed into lpar2rrd crontab:# su - xormon $ crontab -e * * * * * /usr/bin/perl /opt/lpar2rrd-agent/lpar2rrd-agent.pl <XorMon_SERVER.your-domain.com> > /var/tmp/lpar2rrd-agent.out 2>&1
Replace <XorMon_SERVER> by hostname of your XorMon server.
Use preferably FDQN in XorMon hostname, hostname only might have a problem with resolving.
In case you want to direct the agent data to more servers (or ports) add second or more hosts on the cmd line
Bellow cfg will collect data once and sends it to 3 Hosts (Host1 port 8162, Host2 port 8162 and Host3 port 7162)
* * * * * /usr/bin/perl /opt/lpar2rrd-agent/lpar2rrd-agent.pl <Host1> <Host2> <Host3>:7162 > /var/tmp/lpar2rrd-agent.out 2>&1
-
You might need to add xormonuser into /var/adm/cron/cron.allow (AIX) or /etc/cron.allow (Linux) under root user if above "crontab -e" fails.
# echo "lpar2rrd" >> /etc/cron.allow
Troubleshooting
Client (agent) side:- AIX 7.3 TL3+ Dynatrace OneAgent coexistence, read more
-
Test if communication through the LAN is allowed.
$ telnet <XorMon_SERVER> 8162 Connected to 192.168.1.1 . Escape character is '^]'.
This is ok, exit either Ctrl-C or ^].
-
Check following agent files:
data store: /var/tmp/lpar2rrd-agent-*.txt
error log: /var/tmp/lpar2rrd-agent-*.err
output log: /var/tmp/lpar2rrd-agent.out
-
run the agent from cmd line:
$ /usr/bin/perl /opt/lpar2rrd-agent/lpar2rrd-agent.pl -d <XorMon_SERVER.your-domain.com> ... Agent send : yes : forced by -d Agent send slp: sending wait: 4 OS/HMC agent working for server: <XorMon_SERVER> store file for sending is /var/tmp/lpar2rrd-agent-<XorMon_SERVER.your-domain.com>-lpar2rrd.txt
It means that data has been sent to the server, all is fine
Here is example when the agent is not able to sent data :$ /usr/bin/perl /opt/lpar2rrd-agent/lpar2rrd-agent.pl -d <XorMon_SERVER.your-domain.com> ... Agent send : yes : forced by -d Agent send slp: sending wait: 1 OS/HMC agent working for server: <XorMon_SERVER> store file for sending is /var/tmp/lpar2rrd-agent-<XorMon_SERVER>-lpar2rrd.txt Agent timed out after : 50 seconds /opt/lpar2rrd-agent/lpar2rrd-agent.pl:265
It means that the agent could not contact the server.
Check communication, port, above telnet example, DNS resolution of the server etc.